Pull Request Analytics
Track pull request patterns and code review effectiveness
GitPulse tracks pull request patterns and metrics to help you understand your team's code review process and collaboration effectiveness.
Pull Request Overview
Pull request analytics provide insights into how your team reviews code, collaborates on changes, and maintains code quality through the review process.
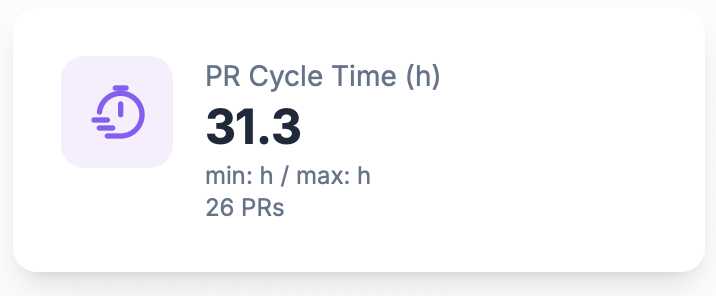
PR Cycle Time
Average Merge Time
The average time between pull request creation and merge, measured in hours. This metric shows how efficiently your team processes pull requests.
What it tells you
- Review process efficiency
- Team responsiveness
- Development workflow speed
Cycle Time Range
The minimum and maximum cycle times show the variability in your review process: - Min: Fastest PR merge time - Max: Slowest PR merge time
What it tells you
- Process consistency
- Bottleneck identification
- Review time variability
Total PRs Processed
The total number of pull requests that have been processed in the selected time period.
What it tells you
- Overall code review volume
- Team collaboration activity
- Feature development pace
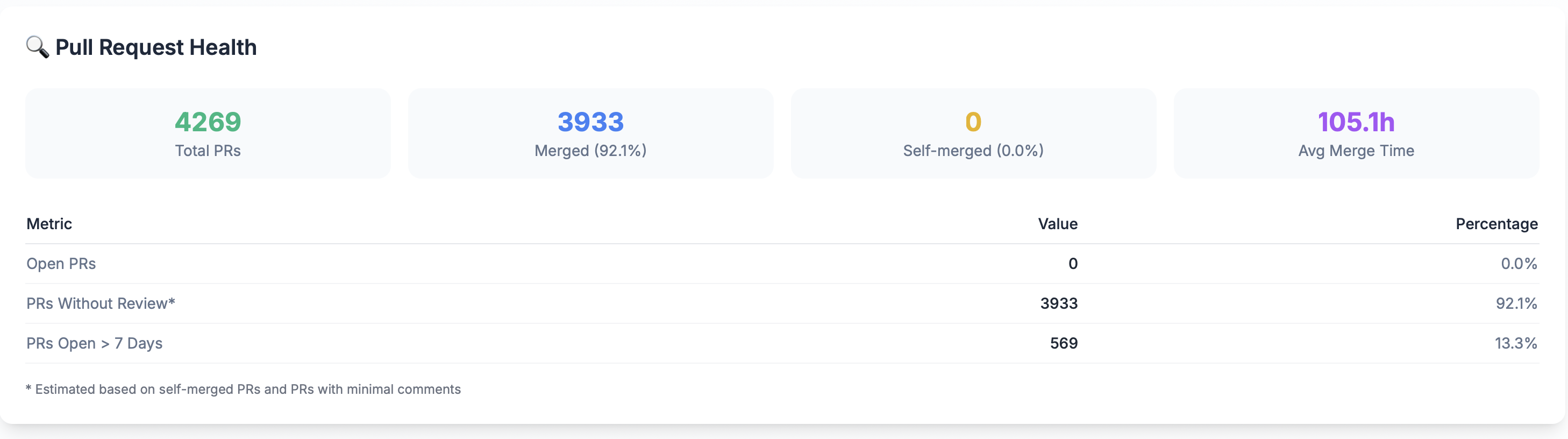
Pull Request Health
Total PRs
The total number of pull requests created in the selected time period.
What it tells you
- Overall code review volume
- Team collaboration activity
- Feature development pace
Merged PRs
The number and percentage of pull requests successfully merged.
What it tells you
- Successful code integration rate
- Development velocity
- Code review effectiveness
Self-Merged PRs
The number and percentage of pull requests merged by the same person who created them.
What it tells you
- Code review compliance
- Team collaboration quality
- Potential bypass of review process
Average Merge Time
The average time it takes to merge pull requests, measured in hours.
What it tells you
- Review process efficiency
- Team responsiveness
- Development workflow speed
PR Health Metrics
Open PRs
The number and percentage of pull requests currently open and awaiting review or merge.
What it tells you
- Current review backlog
- Team review capacity
- Code review efficiency
PRs Without Review
The number and percentage of pull requests that were merged without receiving any reviews.
What it tells you
- Code review compliance
- Quality assurance gaps
- Process bypass patterns
PRs Open > 7 Days
The number and percentage of pull requests that have been open for more than 7 days.
What it tells you
- Review bottlenecks
- Process inefficiencies
- Potential stale PRs
PR Health Indicators
Good signs
- High merge rate (>90%)
- Low self-merge rate (<5%)
- Reasonable average merge time (<24h)
- Low percentage of PRs without review
- Few PRs open for extended periods
Concerning patterns
- High self-merge rate
- Long average merge times
- Many PRs without review
- High number of stale PRs (>7 days)
- Low overall merge rate
Using PR Data
For Development Teams
- Review Process: Monitor cycle times and review coverage
- Collaboration: Track self-merge vs. team review patterns
- Quality Assurance: Ensure PRs receive proper reviews
- Workflow Optimization: Identify bottlenecks in review process
For Management
- Process Efficiency: Assess review workflow effectiveness
- Team Collaboration: Monitor review participation
- Quality Control: Track review compliance
- Capacity Planning: Understand review workload and bottlenecks
Best Practices
Improving PR Process
- Review Requirements: Establish mandatory review policies
- Timely Reviews: Set expectations for review response times
- Quality Feedback: Encourage constructive review comments
- Process Monitoring: Track and address bottlenecks
Team Collaboration
- Review Rotation: Distribute review workload evenly
- Knowledge Sharing: Use reviews for learning and mentoring
- Clear Guidelines: Establish PR creation and review standards
- Regular Reviews: Assess and improve the PR process
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
High Self-Merge Rate
- Cause: Developers bypassing review process
- Solution: Establish mandatory review policies and training
Long Cycle Times
- Cause: Slow review responses or insufficient reviewers
- Solution: Set review time expectations and increase reviewer capacity
Many PRs Without Review
- Cause: Insufficient review requirements or process bypass
- Solution: Implement mandatory review policies and monitoring
Stale PRs (>7 days)
- Cause: Review bottlenecks or abandoned PRs
- Solution: Regular PR cleanup and review process optimization
Getting Help
- Process Reviews: Regularly assess PR workflow effectiveness
- Team Training: Provide review best practices and guidelines
- Tool Configuration: Ensure PR tools support your process
- Feedback Loops: Gather team input on process improvements