Cross-Team Collaboration
Measure inter-team collaboration patterns across project repositories
GitPulse analyzes pull request interactions between different teams within your project, providing insights into cross-team collaboration effectiveness and knowledge sharing patterns.
Cross-Team Collaboration Overview
Cross-team collaboration metrics track how different teams within your project interact through pull requests, revealing collaboration patterns, knowledge sharing, and potential silos that may impact project success.
Collaboration Metrics
Inter-Team PR Activity
Measures the frequency and quality of pull request interactions between different teams:
- Cross-Team Reviews: PRs reviewed by members of different teams
- Cross-Team Contributions: PRs created by one team and reviewed by another
- Knowledge Transfer: PRs that facilitate knowledge sharing between teams
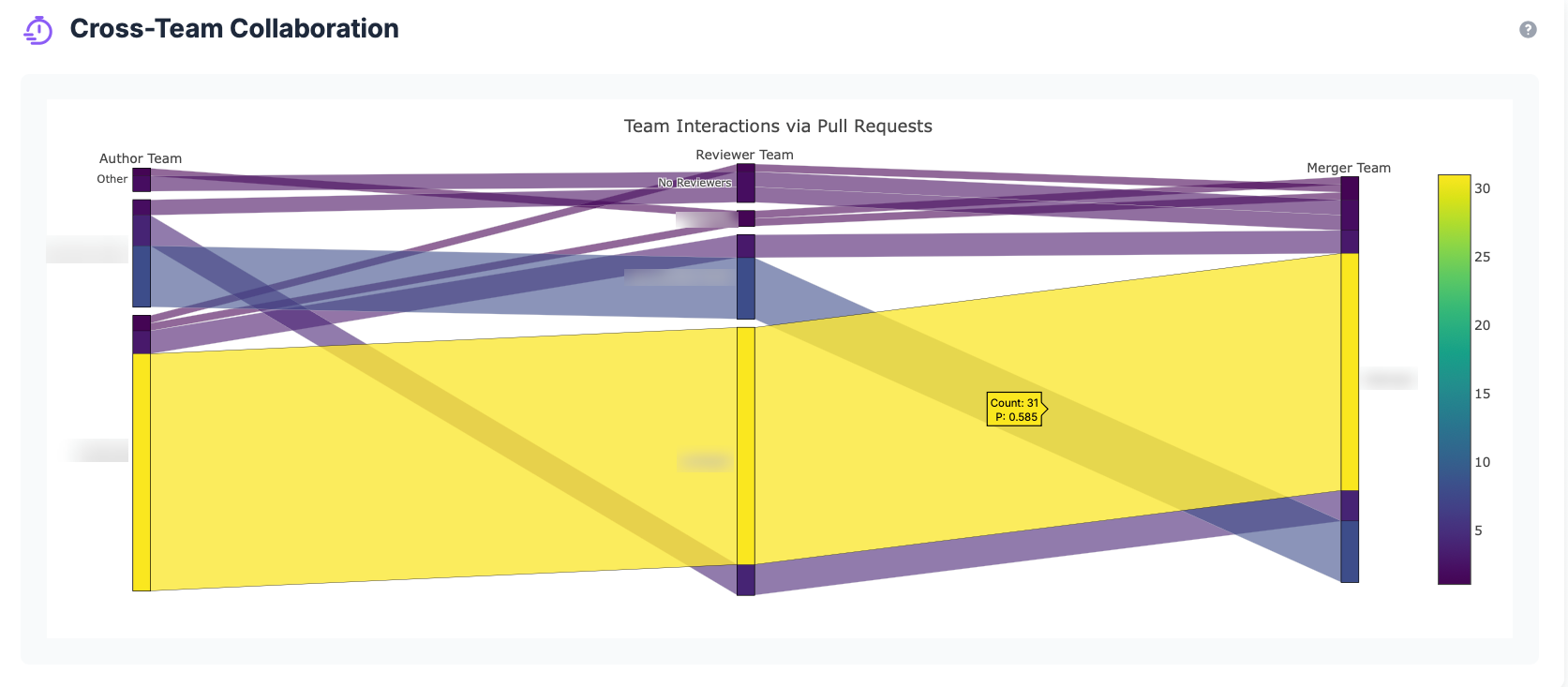
What it tells you
- How frequently teams collaborate across repositories
- Quality of knowledge sharing between teams
- Potential collaboration bottlenecks or silos
Team Interaction Patterns
Analyzes the flow of collaboration between different teams:
- Bidirectional Collaboration: Teams that both review each other's work
- Unidirectional Patterns: Teams that primarily give or receive reviews
- Collaboration Density: How interconnected your teams are
What it tells you
- Balance of collaboration between teams
- Teams that may be isolated or overburdened
- Overall project collaboration health
Repository Cross-Pollination
Tracks how teams contribute to repositories outside their primary domain:
- Cross-Repository Contributions: Teams contributing to other teams' repositories
- Domain Expertise Sharing: Specialized knowledge being shared across teams
- Technical Debt Collaboration: Teams helping with maintenance across repositories
What it tells you
- How well teams understand the broader project architecture
- Level of technical knowledge sharing
- Cross-functional collaboration effectiveness
Collaboration Quality Indicators
Review Quality Metrics
Measures the depth and effectiveness of cross-team reviews:
- Review Comment Density: Quality and quantity of feedback in cross-team reviews
- Review Cycle Time: How quickly cross-team reviews are completed
- Follow-up Engagement: Teams responding to and acting on cross-team feedback
What it tells you
- Quality of cross-team knowledge transfer
- Effectiveness of inter-team communication
- Commitment to collaborative improvement
Knowledge Sharing Patterns
Analyzes how expertise flows between teams:
- Expertise Distribution: How specialized knowledge spreads across teams
- Mentoring Relationships: Teams helping each other learn and grow
- Best Practice Adoption: Teams adopting practices from other teams
What it tells you
- Learning culture within the project
- Innovation and improvement adoption
- Team development and growth patterns
Collaboration Health Indicators
Good signs
- High cross-team review participation (>30% of PRs)
- Balanced bidirectional collaboration between teams
- Quick response times for cross-team reviews (<24h)
- Rich feedback and discussion in cross-team PRs
- Teams contributing to repositories outside their domain
- Consistent knowledge sharing patterns
- Low team isolation metrics
Concerning patterns
- Low cross-team collaboration (<10% of PRs)
- Unidirectional collaboration patterns (teams only giving or receiving)
- Long delays in cross-team review responses
- Minimal feedback in cross-team reviews
- Teams working in complete isolation
- High team silo formation
- Lack of cross-repository contributions
Ideal Collaboration Patterns
Balanced Knowledge Flow
What it looks like: Teams regularly review each other's work, with bidirectional knowledge sharing and mutual learning opportunities.
Why it matters: Ensures no single team becomes a bottleneck or single point of failure, while promoting continuous learning and improvement across the project.
Cross-Functional Expertise
What it looks like: Team members contribute to repositories outside their primary domain, bringing fresh perspectives and preventing knowledge silos.
Why it matters: Builds resilience, improves code quality through diverse perspectives, and ensures better understanding of the overall project architecture.
Proactive Knowledge Sharing
What it looks like: Teams actively share best practices, architectural decisions, and technical insights through collaborative PRs and reviews.
Why it matters: Accelerates project-wide learning, reduces duplication of effort, and ensures consistent quality standards across all repositories.
Strategic Benefits
Risk Mitigation
Reduced Single Points of Failure: When multiple teams understand different parts of the system, the project becomes more resilient to team changes or absences.
Knowledge Redundancy: Critical knowledge is distributed across teams, reducing the risk of losing important expertise.
Innovation and Quality
Diverse Perspectives: Cross-team collaboration brings different viewpoints to problem-solving, leading to better solutions and higher code quality.
Best Practice Propagation: Successful practices from one team can quickly spread to others, improving overall project standards.
Team Development
Skill Development: Team members learn from each other, developing broader technical skills and understanding of the entire project.
Mentoring Opportunities: Experienced team members can mentor others across team boundaries, accelerating growth.
Using Collaboration Data
For Project Managers
- Team Coordination: Identify teams that need better integration
- Resource Allocation: Understand collaboration bottlenecks and capacity needs
- Process Improvement: Optimize cross-team workflows and communication
- Risk Assessment: Identify potential knowledge silos and single points of failure
For Engineering Leaders
- Architecture Decisions: Ensure architectural knowledge is shared across teams
- Code Quality: Monitor how cross-team reviews improve overall code quality
- Team Development: Track skill development and knowledge sharing
- Innovation: Identify opportunities for cross-team innovation and improvement
For Individual Teams
- Collaboration Opportunities: Identify teams to collaborate with for mutual benefit
- Knowledge Gaps: Understand areas where the team could benefit from external expertise
- Contribution Opportunities: Find ways to contribute to other teams' repositories
- Learning Goals: Set objectives for cross-team learning and skill development
Best Practices
Encouraging Cross-Team Collaboration
- Review Rotation: Implement policies that encourage cross-team reviews
- Knowledge Sharing Sessions: Regular sessions where teams share their work and learnings
- Cross-Training: Opportunities for team members to work temporarily with other teams
- Architecture Reviews: Regular cross-team reviews of architectural decisions
Measuring Success
- Collaboration Metrics: Track cross-team PR participation and quality
- Knowledge Distribution: Monitor how expertise spreads across teams
- Response Times: Ensure cross-team reviews are timely and effective
- Outcome Quality: Measure the impact of cross-team collaboration on code quality
Troubleshooting
Common Issues
Low Cross-Team Collaboration
- Cause: Teams working in isolation, lack of awareness of other teams' work
- Solution: Implement cross-team review requirements and knowledge sharing sessions
Unidirectional Collaboration
- Cause: Some teams always giving reviews, others always receiving
- Solution: Balance review responsibilities and encourage bidirectional collaboration
Slow Cross-Team Reviews
- Cause: Teams not prioritizing cross-team work, unclear expectations
- Solution: Set clear expectations and make cross-team collaboration a priority
Poor Quality Cross-Team Reviews
- Cause: Lack of context about other teams' domains, insufficient time allocated
- Solution: Provide better context sharing and allocate dedicated time for cross-team reviews
Getting Help
- Collaboration Workshops: Organize sessions to improve cross-team collaboration skills
- Process Reviews: Regularly assess and improve cross-team collaboration processes
- Tool Configuration: Ensure tools support effective cross-team collaboration
- Culture Building: Foster a culture that values and rewards cross-team collaboration